Deploying Ruby on Rails in Kubernetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Deploying Ruby on Rails in Kubernetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
- Brief overview of Ruby on Rails and Kubernetes.
- Benefits of deploying Rails applications in K8S.
1. Setting Up the Kubernetes Environment
- Prerequisites for Kubernetes setup.
- Creating a Kubernetes cluster.
2. Containerizing the Ruby on Rails Application
- Dockerizing a Rails app.
- Writing a Dockerfile for Rails.
- Building and pushing the Docker image to a registry.
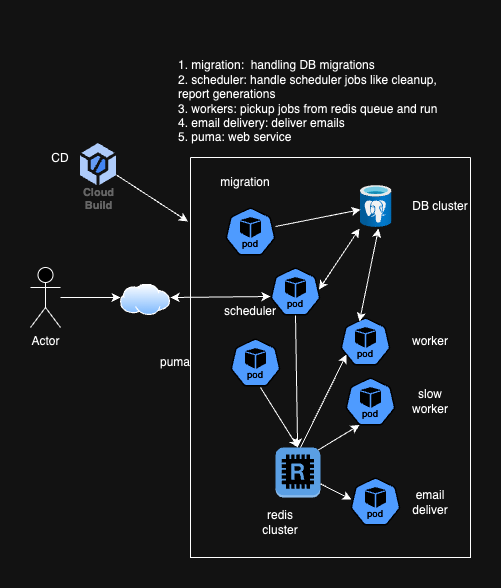
components
1. Handling Database Migrations
- Understanding the importance of database migrations in Rails.
- Strategies for running migrations in a K8S environment.
- Using Init Containers.
- Ensuring idempotency of migrations.
- Example of a migration job definition in K8S.
2. Scheduler Jobs for Maintenance Tasks
- Introduction to background job processing in Rails.
- Implementing a scheduler for periodic tasks.
- Using Kubernetes CronJobs.
- Configuring the scheduler for cleanup and report generation.
- Example of a CronJob YAML file.
3. Workers for Background Processing
- Overview of background workers in Rails.
- Using Sidekiq or Resque for job processing.
- Scaling workers in K8S.
- Deployment configurations.
- Auto-scaling based on queue length.
4. Managing Email Delivery
- Importance of reliable email delivery in web applications.
- Configuring Action Mailer for K8S.
- Using SMTP or a third-party service.
- Securing email delivery with environment variables.
5. Puma as the Web Server
- Introduction to Puma and its role in Rails applications.
- Configuring Puma for K8S.
- Deployment strategies.
- Load balancing and scaling with K8S services.
Deployment
1. Deploying the Application
- Creating Kubernetes manifests for the Rails app.
- Using Helm charts for deployment automation.
- Applying the manifests to the cluster.
2. Monitoring and Logging
- Implementing monitoring solutions for K8S.
- Setting up logging and log aggregation.
3. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
- Integrating K8S with CI/CD pipelines.
- Automating deployment with Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions.
4. Security Considerations
- Securing Rails applications in K8S.
- Using Kubernetes secrets and config maps.
- Network policies and service meshes.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.